Advertisement
Gaps in time series disrupt predictions and reduce model accuracy. Lost information can be recovered with the aid of machine learning. Incomplete records, logging mistakes, or sensor malfunctions can all result in missing values. Unresolved gaps undermine both the accuracy and reliability of forecasts. Data professionals and researchers deal with this issue daily. Machine learning fills gaps efficiently without requiring manual fixes.
There are several approaches, ranging from basic interpolation to sophisticated deep learning. The type of data and business requirements determine which approach is best. Proper handling enhances insights and forecasts. Teams are more confident in their analysis when they are aware of these methods. Structured methods in ML make handling missing information more consistent. This article examines useful machine learning techniques for addressing gaps in time-series data.

Transmission failures or device errors frequently cause gaps in time-series data. Missing values can be sporadic or exhibit trends, like seasonal outages. The source of missing values guides the choice of repair technique. Eliminating gaps alone could result in a smaller dataset and poorer model performance. Rather, learning strategies can aid in recovering valuable insights. Analysts must weigh variables, frequency, and sequence length before selecting a method.
Checking the quality of the data before modeling saves time later. In the fields of finance, healthcare, weather, and industrial monitoring, missing values can happen. Fair comparisons across time periods are ensured by consistent handling. A thorough start enhances forecasts and lessens model bias. Gaps reduce predictive modeling to conjecture in the absence of careful planning and analysis. The first crucial step to success is handling missing values.
Imputation is the process of using estimates to fill in the gaps. The mean method substitutes overall averages for missing values. Because it can withstand outliers, the median replacement method is better at handling extreme values. The gap-filling mode is effective for sequences that lack categorical data. Backward fill uses the next known value, whereas forward fill copies the previous value into the gap.
These quick methods risk distorting underlying time-series patterns. A common flaw is assuming data stability, which often does not align with reality. These methods are suitable for addressing sporadic, small gaps. Large gaps necessitate more sophisticated techniques. For speed, analysts often begin with value estimation before proceeding to more advanced models. The sensitivity of models to data changes is demonstrated by testing various value-filling techniques. Despite their limits, quick fixes provide a practical starting point for analysis.

Intermediate value estimation uses existing points to fill in null values. Linear estimation fills gaps by drawing a straight line between two known values. Complex trends over time are captured by polynomial curve fitting, which fits curves to data. Spline-based curve fitting creates smoother transitions in irregular data. Continuous processes, such as temperature, energy, or sales flow, are frequently included in time series.
Interpolation works best when the data shows a steady progression. Data smoothing, however, assumes that known points will behave predictably. It could result in erroneous patterns in uncertain settings. Estimation between points maintains trend accuracy and yields realistic values for short gaps. It is used in sensors and industrial data by scientists, engineers, and analysts. The approach is simple to use and requires little computing power. In-between prediction cannot replace data when entire sections are missing. Nevertheless, for continuous variables with brief missing spans, it is a reliable option.
Machine learning models use patterns in the available data to forecast missing values. Regression models use the relationships between variables to estimate gaps. K-nearest neighbors recommend replacements by identifying comparable historical values. Decision trees assign values to the gaps in sequences by segmenting them into rules. By combining several weak learners, ensemble techniques like random forest increase reliability. The addition of extra features, such as seasonality or external data, enhances the capabilities of machine learning.
Accuracy increases as models learn structure beyond simple averages. For training to be practical, there must be sufficient complete data. Cross-validation ensures stability while filling in the gaps. Compared to trend fitting or simple missing-value treatment, these models are more accurate. They strike a balance between improved forecasts and complexity. Businesses prefer these methods for moderately gapped predictive tasks. Machine learning models facilitate the effective handling of incomplete sequences.
Deep learning provides powerful methods for handling incomplete time-series data. Sequences are learned by recurrent neural networks, which also produce values for blank spaces. Long gaps are better handled by long short-term memory networks, which utilize memory cells to store information over extended periods. Gated recurrent units also model dependencies over time. Convolutional networks enhance fine-grained estimates by capturing local patterns. Autoencoders compress data and recreate missing parts to reconstruct time series.
Standard approaches frequently overlook the nonlinear relationships used by deep models. These models require large datasets and significant computing resources. These models perform well in domains such as finance or healthcare, where data has intricate dependencies. The accuracy of deep learning frequently surpasses that of simple models. The trade-offs include longer training times and higher operational costs. Analysts must rigorously test architectures to avoid overfitting. Deep techniques are still a strong choice for sophisticated empty entries recovery.
Hybrid approaches combine different techniques to handle missing data more effectively. For small gaps, analysts frequently start with simple imputation. Values for continuous sections may then be refined through interpolation. Where patterns are found, machine learning models add predictions. Long sequences with nonlinear behavior are handled by deep learning. Blending techniques reduces dependence on any single method.
Ensemble learning combines predictions from multiple models for stronger results. Before finalization, testing the output of each method guarantees stability. Industry experts often employ hybrid strategies for complex tasks, such as energy or climate forecasting. No single technique is optimal for all datasets. Combinations are chosen based on business objectives, time, and resources. Combining methods lowers error and increases flexibility. Blended approaches prepare time-series data for more accurate and reliable ML applications. By complementing each other, these methods increase reliability and produce more stable results.
Machine learning techniques reduce the challenges caused by incomplete time-series data. Every technique, from fast imputation to sophisticated deep learning, has advantages. Accuracy is often enhanced by combining multiple strategies. Analysts must weigh performance, simplicity, and resources when selecting a solution. Time-series gaps become insurmountable with careful application. Correct handling of data loss enables teams to produce more accurate forecasts and insights. Predictions gain credibility when they are handled well. Businesses can maintain their competitiveness and knowledge by implementing the proper strategy.
Advertisement

How the Bamba: Inference-Efficient Hybrid Mamba2 Model improves AI performance by reducing resource demands while maintaining high accuracy and speed using the Mamba2 framework

Is self-driving tech still a future dream? Not anymore. Nvidia’s full-stack autonomous driving platform is now officially in production—and it’s already rolling into real vehicles

Intel and Hugging Face are teaming up to make machine learning hardware acceleration more accessible. Their partnership brings performance, flexibility, and ease of use to developers at every level
The future of robots and robotics is transforming daily life through smarter machines that think, learn, and assist. From healthcare to space exploration, robotics technology is reshaping how humans work, connect, and solve real-world challenges
Advertisement

EY introduced its Nvidia AI-powered contract analysis at Mobile World Congress, showcasing how advanced AI and GPU technology transform contract review with speed, accuracy, and insight

Microsoft has introduced stronger safeguards and policies to tackle malicious Copilot AI use, ensuring the tool remains safe, reliable, and aligned with responsible AI practices
How the OpenAI jobs platform is changing the hiring process through AI integration. Learn what this means for job seekers and how it may reshape the future of work

Find the top eight DeepSeek AI prompts that can accelerate your branding, content creation, and digital marketing results.
Advertisement

How Amazon S3 works, its storage classes, features, and benefits. Discover why this cloud storage solution is trusted for secure, scalable data management
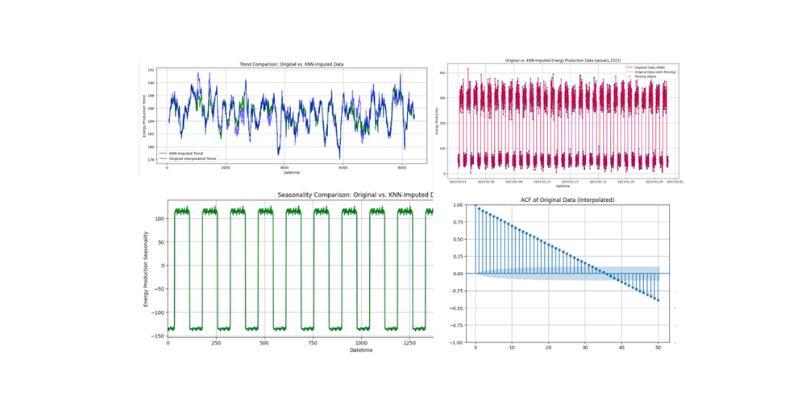
Discover effective machine learning techniques to handle missing data in time-series, improving predictions and model reliability

Curious about ChatGPT jailbreaks? Learn how prompt injection works, why users attempt these hacks, and the risks involved in bypassing AI restrictions
Explore Apache Kafka use cases in real-world scenarios and follow this detailed Kafka installation guide to set up your own event streaming platform