Advertisement
Yamaha, long recognized for motorcycles and musical instruments, has turned its focus to an unexpected area — farming. The company recently launched a new division dedicated to autonomous farming technology, bringing its mechanical and robotics expertise to agriculture. This step shows Yamaha’s commitment to addressing modern farming challenges like labor shortages, rising costs, and environmental concerns.
The new division is set to design machines that ease repetitive tasks while remaining approachable for farmers of all backgrounds. With practical solutions rooted in real needs, Yamaha is looking to help farmers work smarter and more efficiently in an increasingly demanding industry.
Yamaha's entry into autonomous farming builds on years of experience making agricultural equipment, particularly in Japan, where its compact tractors and drones are already trusted by farmers. This new division builds upon that foundation, focusing squarely on fully automated tools designed to fit the realities of modern farming. The goal is clear: to create dependable machines that handle repetitive, time-consuming tasks, allowing farmers to step back from the grind and focus on managing their land more effectively.
This shift mirrors a broader change happening in agriculture worldwide, as technology companies look for ways to help a sector stretched by shrinking labor pools and growing demand for productivity. Yamaha brings a strong background in precision engineering, which it’s applying to new solutions like GPS-guided tractors, machine-vision systems, and on-board data tools already in development. But it's not just about cutting-edge tech for its own sake. Yamaha is working to keep these machines intuitive and straightforward, so farmers don't need advanced training to use them. By prioritizing practicality and ease of adoption, Yamaha aims to make automation an accessible and everyday part of farming.
At the core of Yamaha's initiative is its knowledge of robotics, developed through decades of creating high-performance products in other industries. This expertise translates naturally to agriculture, where machines are already necessary but still very reliant on human input. The firm wants to produce machinery that not only replaces man but also changes the manner in which activities are carried out, with greater precision and less waste.
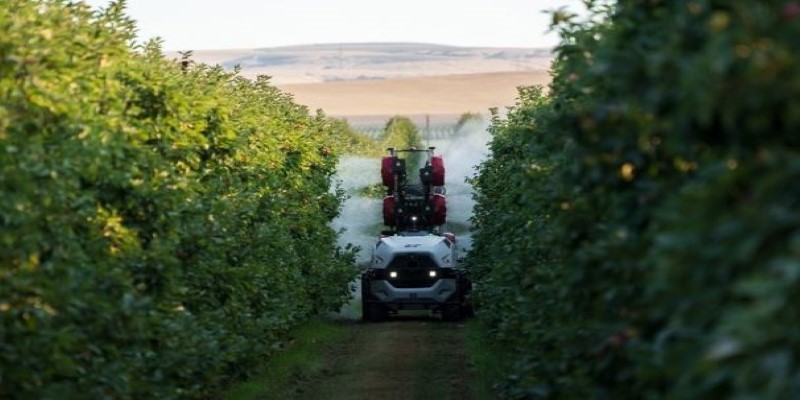

Current prototypes include self-driving tractors capable of navigating rows with accuracy and drones that can monitor plant health and soil conditions from the air. These designs aim to function reliably across varying climates and terrains, which is critical for farming. Yamaha has been engaging with farmers directly to ensure that the machines meet the practical needs of day-to-day work. Rather than focusing purely on technological capabilities, the company is paying close attention to usability and effectiveness in real-world conditions.
The potential benefits of robotic farming go beyond saving time and labor. Integrated sensors and connectivity allow these machines to gather data about crop growth, moisture levels, and pest activity. This information helps farmers make better-informed decisions about when and where to apply treatments or adjust schedules, improving yields and reducing unnecessary inputs. With remote monitoring via smartphones or computers, farmers can stay informed and in control without being physically present for every task, which adds flexibility to their routines.
Yamaha’s autonomous farming division arrives at a time when agriculture is grappling with significant changes. In many regions, fewer young people are choosing to work in the sector, leaving older farmers to manage large areas with shrinking labor pools. Rising input prices and unpredictable weather patterns put even more strain on farmers to achieve higher efficiency.
Autonomous machines can help alleviate these pressures by making it possible to maintain productivity with fewer workers. Time savings are an immediate benefit, as automated equipment can cover more ground in less time and keep working under conditions that might slow humans down. Precision farming methods enabled by automation also reduce waste by targeting treatments and resources only where they’re needed. This not only cuts costs but also limits environmental impacts, which has become a growing concern for the industry.
For the broader agricultural market, Yamaha’s presence adds competition and variety. Farmers may feel more confident trying automation if they see recognizable names like Yamaha bringing their reputation for reliable machinery into the field. As more farmers adopt these technologies, the entire supply chain — from equipment dealers to maintenance services — is likely to evolve, creating new opportunities and support networks tailored to autonomous farming.
While Yamaha’s autonomous farming vision is promising, there are still hurdles to overcome. Agricultural conditions vary widely from region to region, and creating machines that perform reliably across different crops, soils, and climates remains complex. Farmers who are unfamiliar with automated systems may hesitate to invest in them if they perceive the costs as high or the operation as difficult. Yamaha is aware of these concerns and is focusing on making its products affordable and straightforward to use.
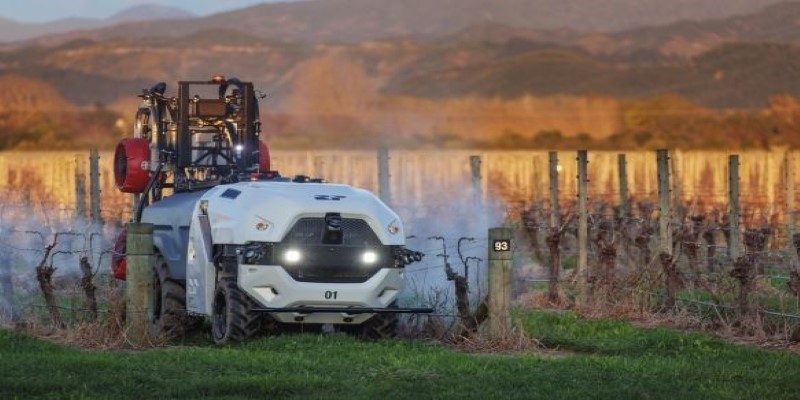

Another consideration is regulation. Rules about how autonomous vehicles can operate in agricultural environments differ between countries, and issues such as safety and data privacy will need careful attention. Yamaha has said it is working with regulators to ensure its equipment meets all local requirements and can be deployed without unnecessary delays.
Looking forward, Yamaha is expected to expand beyond its initial products. Plans may include more specialized robotic harvesters, automated irrigation systems that adjust in real-time, and even partnerships with other tech firms to integrate artificial intelligence into farming decisions. As automation becomes more advanced, machines will likely become better at interpreting conditions and responding flexibly, further lightening the load for farmers and making operations more productive.
Yamaha's creation of a division dedicated to autonomous farming marks a thoughtful response to the challenges facing today's farmers. With a clear focus on practical, reliable machines designed to fit seamlessly into daily work, the company brings its engineering skills to a sector in need of fresh solutions. By reducing labor demands, improving precision, and making it easier to manage farms of all sizes, autonomous farming has the potential to support farmers while protecting their livelihoods. Yamaha’s move suggests a future where technology works quietly alongside farmers, helping them meet growing demands while preserving the human care that farming has always required.
Advertisement
Explore the current state of quantum computing, its challenges, progress, and future impact on science, business, and technology

Learn 5 simple steps to protect your data, build trust, and ensure safe, fair AI use in today's digital world.

Intel and Hugging Face are teaming up to make machine learning hardware acceleration more accessible. Their partnership brings performance, flexibility, and ease of use to developers at every level

How Nvidia produces China-specific AI chips to stay competitive in the Chinese market. Learn about the impact of AI chip production on global trade and technological advancements
Advertisement

How the Philadelphia Eagles Super Bowl win was accurately predicted by AI, showcasing the growing role of data-driven analysis in sports outcomes

Learn the top 8 Claude AI prompts designed to help business coaches and consultants boost productivity and client results.

Learn how to use ChatGPT for customer service to improve efficiency, handle FAQs, and deliver 24/7 support at scale

PaLM 2 is reshaping Bard AI with better reasoning, faster response times, multilingual support, and safer content. See how this powerful model enhances Google's AI tool
Advertisement

How Amazon S3 works, its storage classes, features, and benefits. Discover why this cloud storage solution is trusted for secure, scalable data management

Bias in generative AI starts with the data and carries through to training and outputs. Here's how teams audit, adjust, and monitor systems to make them more fair and accurate

AI content detectors don’t work reliably and often mislabel human writing. Learn why these tools are flawed, how false positives happen, and what smarter alternatives look like

Improve your skills (both technical and non-technical) and build cool projects to set yourself apart in this crowded job market